Prices Set for New Health-Care Exchanges
< < Go Back
Younger Buyers May Face Higher Insurance Premiums.
U.S. officials for the first time disclosed insurance prices that will be offered through new federally run health-care exchanges starting Oct. 1, showing that young, healthy buyers likely will pay more than they do currently while older, sicker consumers should get a break.
The plans, offered under the health-care overhaul to people who don’t get insurance through an employer or government program, in many cases provide broader coverage than current policies.
Costs will vary widely from state to state and for different types of consumers. Government subsidies will cut costs for some lower-income consumers.
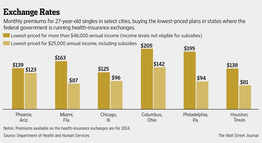
Across the country, the average premium for a 27-year-old nonsmoker, regardless of gender, will start at $163 a month for the lowest-cost “bronze” plan; $203 for the “silver” plan, which provides more benefits than bronze; and $240 for the more-comprehensive “gold” plan.
But for some buyers, prices will rise from today’s less-comprehensive policies.
In Nashville, Tenn., a 27-year-old male nonsmoker could pay as little as $41 a month now for a bare-bones policy, but would pay $114 a month for the lowest-cost bronze option in the new federal health exchanges.
Likewise, the least-expensive bronze policy would rise to $195 a month in Philadelphia for that same 27-year-old, from $73 today. In Cheyenne, Wyo., the lowest-cost option would be $271 a month, up from $82 today.
The Affordable Care Act marks a fundamental shift in the way insurers price their products. Carriers won’t be allowed to charge higher premiums for consumers who have medical histories suggesting they might be more expensive to cover because they need more care. They will have to treat customers equally, with limited variation in premiums based on buyers’ ages or whether they smoke.
Insurers also will have to offer a more generous benefits package that includes hospital care, preventive services, prescription drugs and maternity coverage.
For consumers used to skimpier plans—or young, healthy people who previously enjoyed attractive rates—that could mean significantly higher premiums.
More From The Wall Street Journal (subscription required):