from Maudlin Economics,
5/16/23:
The United States is about to hit its credit limit. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen says the government will have to stop borrowing as soon as June 1 unless Congress raises the debt ceiling.
Depending on who you ask, that could mean anything from “no big deal” to “economic catastrophe.” We somehow survived a similar episode in 2011, but that one ended quickly. Bad things could happen if the politicians can’t make a deal.
No matter how this stand-off ends, it’s already exposed some deep misunderstandings. They matter, too, because we really do have major budgetary challenges. They won’t get solved when the people in charge can’t even speak the same language.
So, let’s get some things straight.
Artificial Ceiling
Commentators often compare the federal budget to a family sitting around the kitchen table, discussing finances.
That’s a nice, relatable but flawed comparison. The federal government isn’t a family. It has entirely different abilities and limitations.
When you borrow money—by getting a credit card, for instance—the lender typically gives you a limit. They want you to borrow so they can earn revenue, but not so much that you can’t repay it. They estimate your ability and set an interest rate high enough to make the risk worthwhile.
The debt ceiling the government is presently approaching is self-imposed by the borrower (Congress). The lenders (i.e., T-bond and T-bill buyers) in this situation are happy to give the Treasury more cash at very low interest rates.
Congressional Doubletalk
The 14th Amendment says the “full faith and credit” of US government debt can’t be questioned. This may override the debt ceiling, but there’s a more practical issue, too.
The Constitution gives Congress “power of the purse,” i.e., the responsibility to set tax and spending policies. The president then executes those policies.
The bills Congress passes (which become law when the president agrees) are actually orders to the president. They are Congress saying, “You will spend certain amounts of money on the things we tell you to buy.”
Presidents can’t ignore Congressional appropriations. They must spend the money as ordered.
What happens when the tax rates Congress sets don’t raise enough revenue, and Congress also won’t raise the debt ceiling to let the president fill the gap?
No one knows. Every option breaks the law. It puts the president in an impossible situation.
This is so ludicrous it may be unconstitutional. Some think President Biden should simply ignore the debt ceiling and issue more debt anyway, even if Congress doesn’t act. But that’s not great either; it would put those particular bonds under a legal cloud, maybe raising interest rates.
Imaginary Cuts
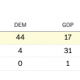
All this is happening because House Republicans say spending is out of control. They passed a bill last month outlining their better ideas.
Because cutting Social Security and other mandatory programs is politically difficult, their savings focus mainly on “discretionary” spending. Their proposal would save $3.2 trillion over 10 years by rolling back spending to 2022 levels, then capping growth at 1% annually.
That sounds reasonable. The problem is they don’t have the power to cut spending 10 years in advance. Nor does anyone else. All spending bills are for one year and one year only.
That’s how our system works. A future Congress can always change anything today’s Congress does. It has to be that way or elections become meaningless.
The Republicans talking about big spending cuts are claiming credit for something purely hypothetical. Ditto for the Democrats who are afraid their favorite domestic programs will face cuts. They probably won’t—at least not for long.
These are political charades having little impact on actual spending policy… which really does deserve a thorough rethink.
More From Maudlin Economics: